GST has been implemented in the Indian tax system, and the first phase of return filing has been successfully concluded on 28th August 2017.
Since GST is such a big system and aims to collect taxes from millions (even billions) of eligible taxpayers in India, it is natural to witness non-compliances, frauds, tax evasion, etc.
Therefore, the government has also devised a proper procedure for the auditing and assessment of tax compliance rating and the recovery rules and provisions for unpaid, late-paid and/or short paid taxes.
Contents
GST Procedures
There are following four basic types of GST procedures:
- Audits
- Assessment
- Demand and Recovery
- Advance Ruling
Audits under GST
This is the process of auditing the records supplied and maintained by registered taxpayers on their GST accounts, to check their validity and accuracy and to assess the tax compliance level.
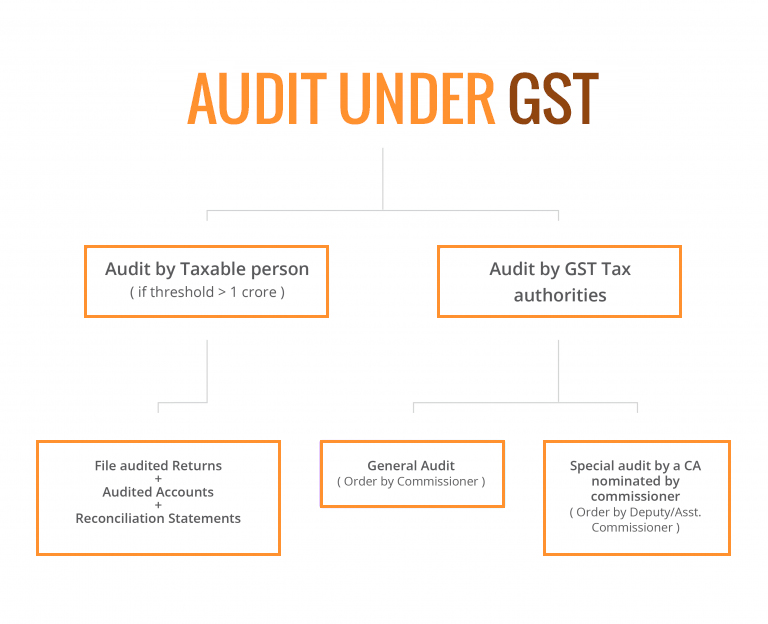
The audit process under GST will be completed in one of the following two ways.
1. Audit by Registered Dealer: Any dealer having an annual turnover above Rs. 1 crore will have to perform the audit himself by hiring a CA or CMA.
2. Audit by GST Authorities: For small dealers, the GST commissioner himself or one of his appointed officials will conduct the General audit.
For complex and/or high revenue cases, the department may choose to conduct a special audit by appointing a CA or CMA for the job.
Assessment under GST
The process of assessment involves the verification of tax liability of a particular taxpayer. There are following 5 types of assessments in GST.
1. Self Assessment: As the name suggests, the process involves every GST registered taxpayer self-assessing his/her tax liability (and penalties, if any), and filing the returns accordingly, for each tax period.
2. Provisional Assessment: In case if a taxpayer is not able to determine the taxable value of his goods/service or find the tax rate for the same, he can request a provisional assessment by one of the GST officials. Then, the person will be allowed to file returns and pay taxes on a provisional basis as instructed by the officer.
3. Scrutiny Assessment: A GST officer, in his own capacity or as instructed by the authorities, can conduct a scrutiny assessment to check the validity and correctness of the return filed by one of the taxpayers. If any discrepancies are found in the return, the officer is allowed to ask for explanations from the particular taxpayer.
4. Summary Assessment: A summary assessment is done when there is no time to conduct a full assessment or if the delay in revealing the tax liability is going to harm the revenue interest. The respective officer, with the permission of the joint/additional GST commissioner, can produce the summary assessment to protect the revenue interest.
5. Best Judgement Assessment: It is done in the following two situations.
- Assessment of no return filing: The proper officer will assess the tax liability according to his best judgment for those taxpayers who have not filed their returns even after receiving a notice.
- Assessment of unregistered taxpayers: The officer will assess the tax liability of the persons who are liable to pay tax but have not obtained a GST registration yet. A notice will be sent to the concerned person.
Demand and Recovery of GST Tax
Based on the findings of the auditing and assessment of tax provisions and liabilities of various taxpayers, a show cause notice will be issued by the proper officer to the guilty taxpayers who have not paid taxes, paid wrong or incomplete taxes and/or claimed incorrect ITC or refunds.
Demands can be requested in any or all of the following cases:
- When tax is unpaid or paid wrong or short
- When a taxpayer collects tax but does not deposit the same to the government
- When CGST/SGST was paid on an IGST applicable supply and vice versa.
If demands are not paid even after the notice, the department can start tax recovery proceedings.
Advance Ruling
The GST has the provision for taxpayers to request advance clarifications from the authorities on specific tax related matters before starting a legal or any other proposed activity. The tax authority will produce a written decision or advance ruling to the applicant clarifying his/her queries on the specific issue.






In this blog, you are providing most important information about GST. Many firms have developed gst app and software for providing latest information which will help to understand business criteria and tax structure.
Nice post. I was checking continuously this blog and I am impressed! Extremely useful information specifically the last part ???? I care for such info much. I was seeking this certain information for a very long time. Thank you and good luck.